Breaking Down Common Mortgage and Interest Rate Terms

There’s a lot that goes into getting approved for a home loan. It can feel like learning a whole new language, particularly for first-time homebuyers.
To help demystify the homebuying process, Alaska Housing Finance Corporation offers free homebuyer education classes to explain everything, including the many acronyms and specialized terms you will likely come across in your homebuying journey.
The following information about mortgages comes from a workbook that homebuyer education participants receive while taking the class.
Two Types of Mortgages
What's the difference between conventional and guaranteed mortgage? Is your rate fixed or adjustable?
There are many names for various mortgage products; however, all mortgages fall under two general types: conventional or government-insured/guaranteed. As a public investor, AHFC offers both conventional and government-insured/guaranteed loans at different interest rates depending on the loan type.
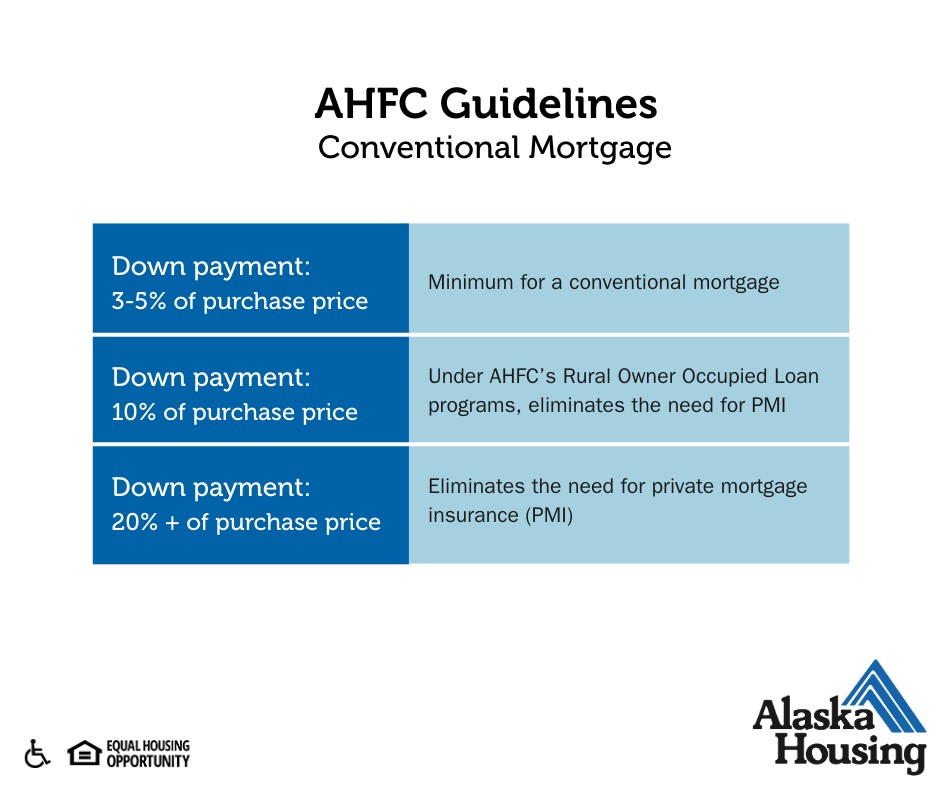
1. Conventional Mortgages
Conventional mortgages are made through a private lender, a business. Freddie Mac or Fannie Mae are the most common conventional, private investors.
A public lender is a lender from the public sector. For example, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), the Dept. of Housing & Urban Development (HUD-184) and the Veteran’s Administration (VA).
To qualify for a conventional mortgage, borrowers typically need a minimum down payment of 3-5% of the total purchase of the home, and they must obtain Private Mortgage Insurance. PMI payments are often required until around 20% of the mortgage is paid off.
Some programs like the Alaska Housing’s Rural Owner-Occupied loan can decrease this PMI requirement for conventional mortgages.
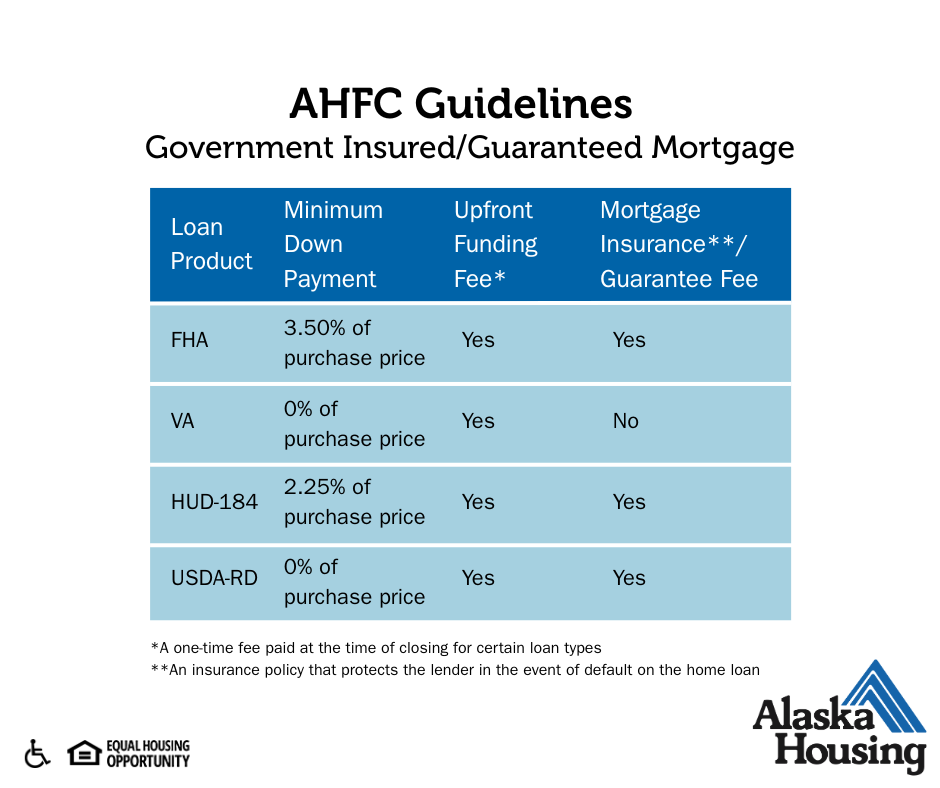
2. Government-Insured Mortgages
A government-insured or guaranteed mortgage is insured by a federal agency like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) or U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). The minimum down payment and credit score requirements on government mortgages are lower but these loans typically have more fees associated with the loan conditions.
Your lender can help you weigh your options and decide which mortgage loan is best for you, based on your income and other factors.
Two Types of Interest Rate Options
Regardless of whether your mortgage is Conventional or Government-Insured, it will also have one of two types of interest rates: fixed or adjustable.
- A fixed rate mortgage keeps the same interest rate throughout the life of the term of the mortgage. A fixed rate mortgage might be right for you if you want:
- Predictable payments.
-
To refinance later if interest rates drop or your credit score improves.
- Adjustable-rate mortgages, also referred to as “variable-rate mortgages”, start with an interest rate below what is available for a fixed rate mortgage. The interest rate is subject to change and may go up or down depending on changes in the index tied to the mortgage. Note that AHFC does not offer adjustable-rate mortgages.
It’s always important to talk to your lender and understand all the terms and conditions of any loan before you make a decision.
Looking to buy a home in Alaska?
Mortgage loans are available from many banks and financial institutions, including from AHFC approved lenders. Through our lender partners, AHFC offers many different home loan types – from loans for first-time homebuyers to multifamily properties.
“Not only does choosing an AHFC home loan mean investing in your home, but it also means investing in Alaska through the dividend contribution AHFC pays to the state.”
– Michelle Graves, AHFC Mortgage Director
To unpack more homebuying terms and tips, sign up for homebuyer education! A class can help you learn how to shop for a lender, get a home loan, understand loan terms and much more. It will also familiarize you with the terminology you’ll hear during the purchase process.
![Alaska Housing Finance Corporation [Logo]](/application/themes/ahf2/images/logo.png?v=2)